All the posts for die-casting-engineering
Posts by Topic
- Die Casting simulation (35)
- Co-design (26)
- Cost reduction (23)
- die casting finishing (18)
- Defects reduction (16)
- high pressure die casting (16)
- die casting process (15)
- VAVE (13)
- die casting (12)
- Zinc (11)
- Zinc benefits (10)
- casting process (10)
- die casting engineering (10)
- optimization (10)
- Innovation (9)
- automotive (8)
- casting (8)
- ZAMAK (7)
- product design (6)
- quality (6)
- Mould Design (5)
- Scrap reduction (5)
- automation (5)
- saving (5)
- Mold (4)
- benefits (4)
- die casting machines (4)
- hot chamber die casting (4)
- industry (4)
- supply chain (4)
- zinc alloys (4)
- Commodity (3)
- coffee market (3)
- mold maintenance (3)
- process improvement (3)
- small appliances (3)
- technology (3)
- thin wall thickness (3)
- Shrinkage porosity (2)
- costs saving (2)
- customer service (2)
- cycle time (2)
- electronic products (2)
- improvement (2)
- metrology (2)
- mold design (2)
- process analysis (2)
- production (2)
- production process (2)
- recycling (2)
- sustainability (2)
- white goods (2)
- zinc life cycle (2)
- DFM (1)
- Electromechanical systems (1)
- HPDC (1)
- Lighting components (1)
- Press (1)
- SME (1)
- Textile (1)
- Textile Machineries (1)
- Zinc alloy actuators (1)
- actuators (1)
- chrome plating (1)
- environment (1)
- industrial machinery (1)
- industrialization (1)
- lead time (1)
- machines (1)
- painting (1)
- quality control (1)
- surface treatment (1)
- tier 2 automotive supplier (1)
- vacuum valve (1)
- zinc alloys for doors and windows (1)
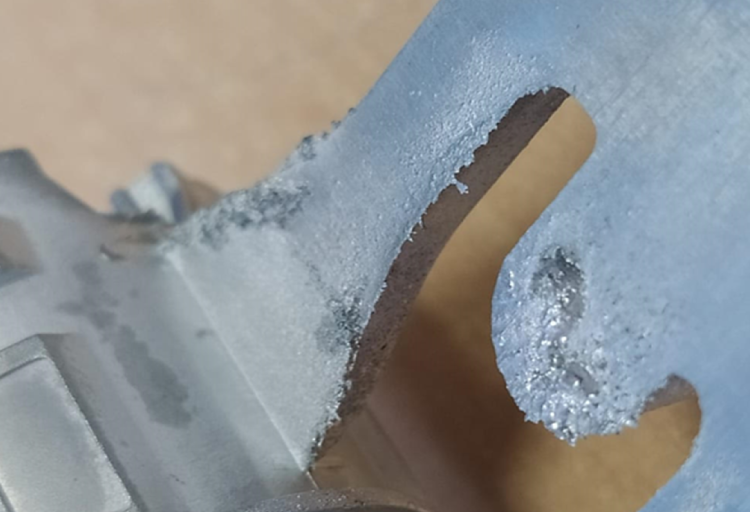
Cavitation is a form of mold erosion that occurs during casting. In some critical areas of the dies, steel is removed and eroded by an aggression generated by micro-implosions of gases and vapors that occur during the filling of the cavity.
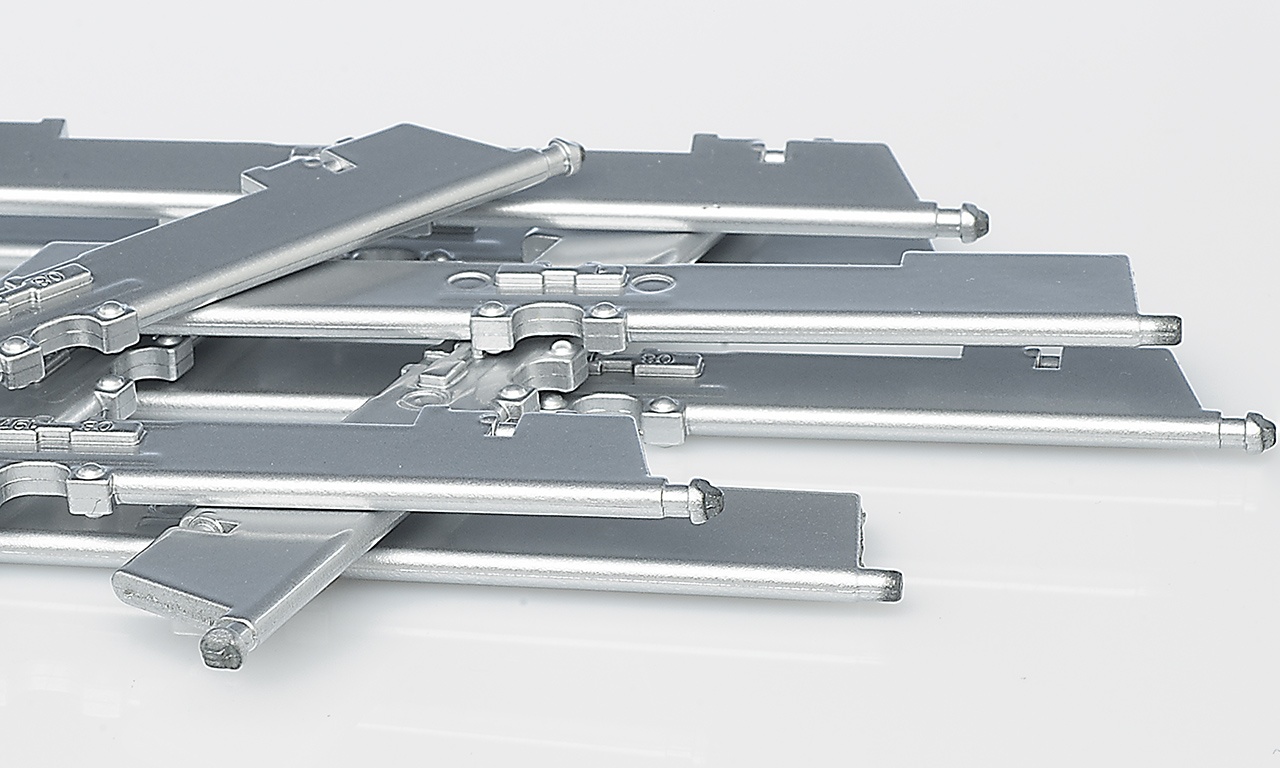
The rapid deterioration of the dies results in production stoppages and major maintenance operations that compromise the production efficiency.
In terms of mechanical strength, the breaking load is commonly defined as ultimate tensile stress (UTS), which is the maximum external force limit applied beyond which a material loses its functional specifications in terms of strength. Tensile strength tests vary according to the type of stress the material is subjected to, which we will describe later. In our case, are tests to be carried out on a component during production.
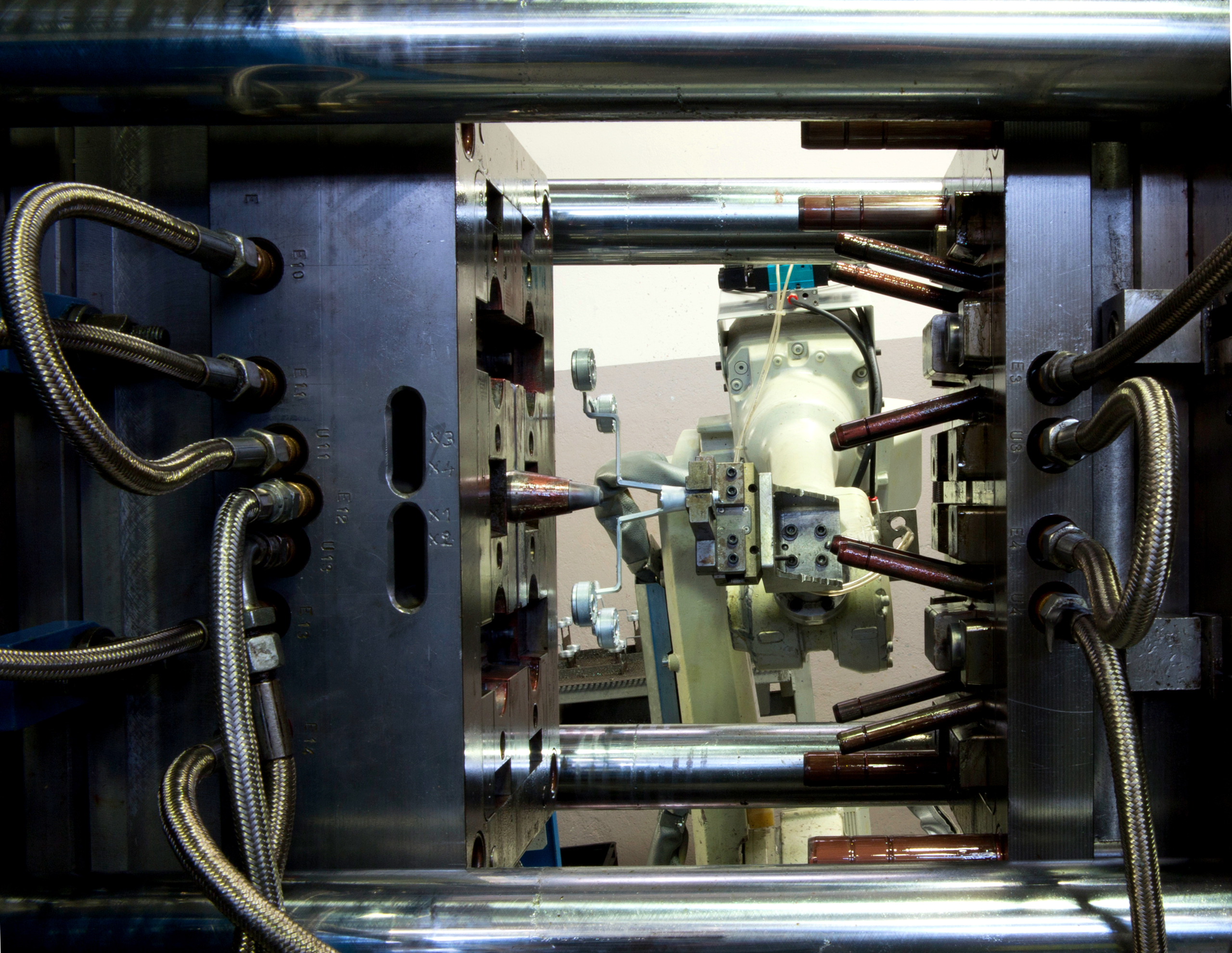
Zinc die casting is a process that consists in injecting the liquid metal under pressure into a mould, generally made of special steel, and letting it solidify. The die casting technique is the shortest way that leads from the metal in the liquid state to the finished product and has different fields of application (automotive above all, but also electronics, electromechanics, household appliances and in general all sectors that require non-ferrous metallic components).
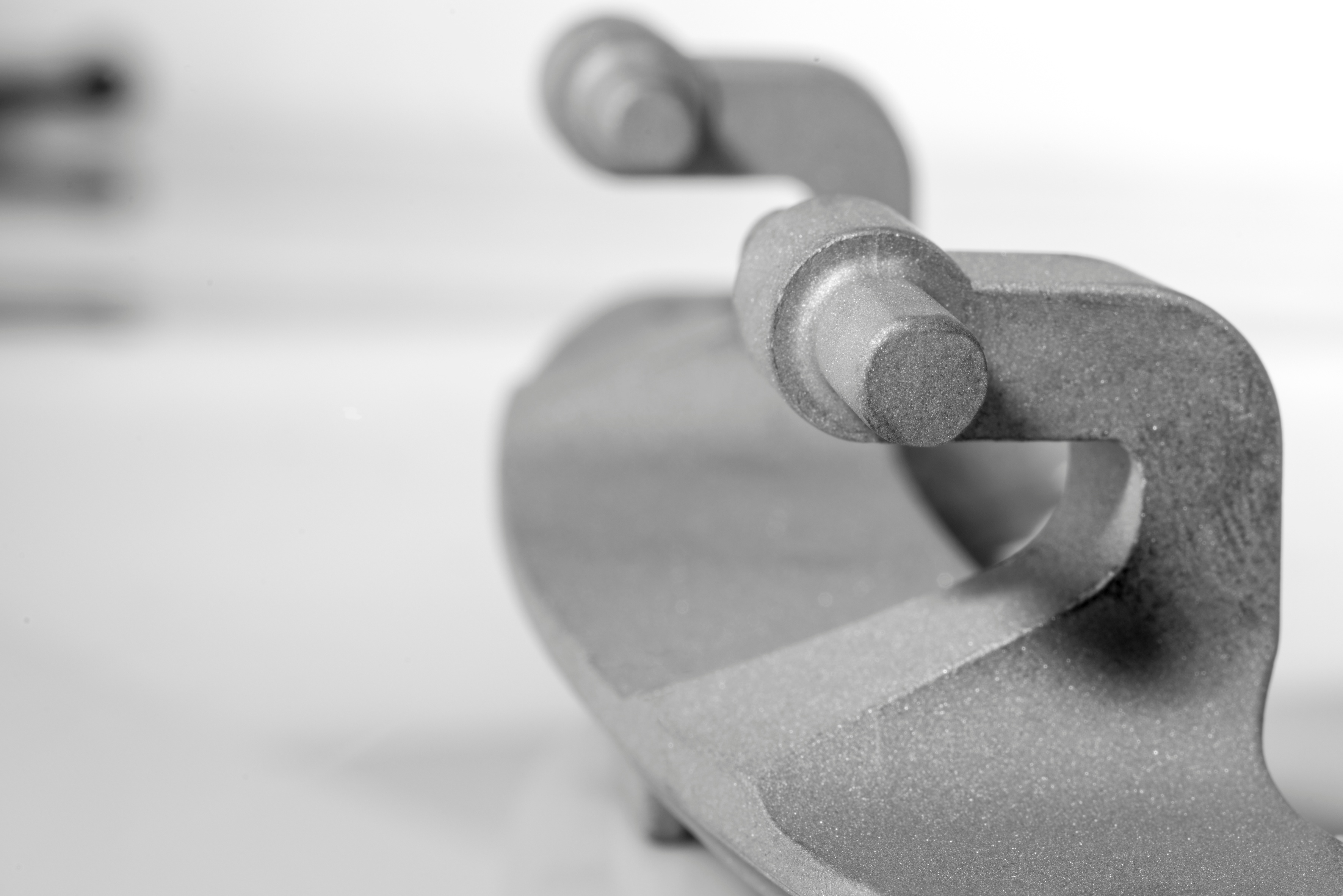
In this post we are going to analyze a case study that explains how to reduce casting defects through mold design. Due to mold wear condition components started to show superficial defects: Bruschi engineers have thus introduced improvements in order to reduce casting defects.
Process improvement, in the zinc die casting industry as well as in many other manufacturing sectors, consists of a series of actions undertaken to enhance production times, to reduce costs and, consequently, to obtain results that satisfy client’s requests in terms of timing and performance.
In this post we are going to explore a case study dedicated to surface aesthetical quality in automotive. This post is part of a series in which we explain the importance of simulation for HPDC (High Pressure Die Casting) through the presentation of real life cases.
In this post we are going to explain what Value Analysis / Value Engineering is, starting from its history up to why it is so important for manufacturers today.
In this post we are going to describe the designing process of a hot chamber injection system, useful for casting process optimization.
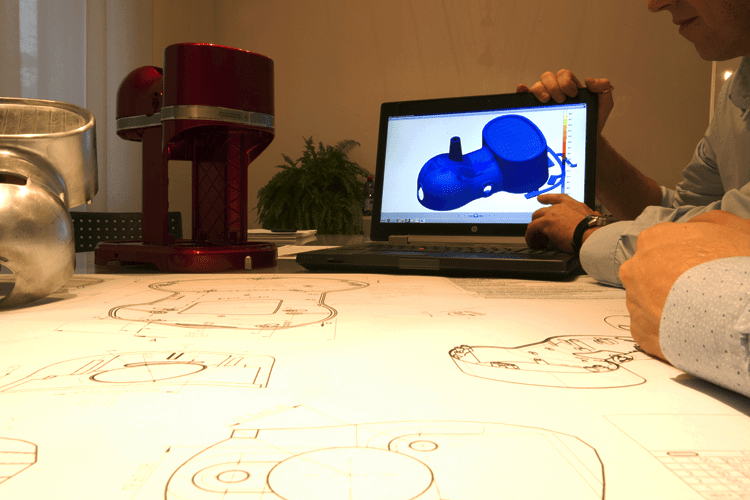
In this article we are going to analyze product design for die casting through the study of a DFM (Design for Manufacturability) and suggesting a way to optimize and speed up the process: co-design.
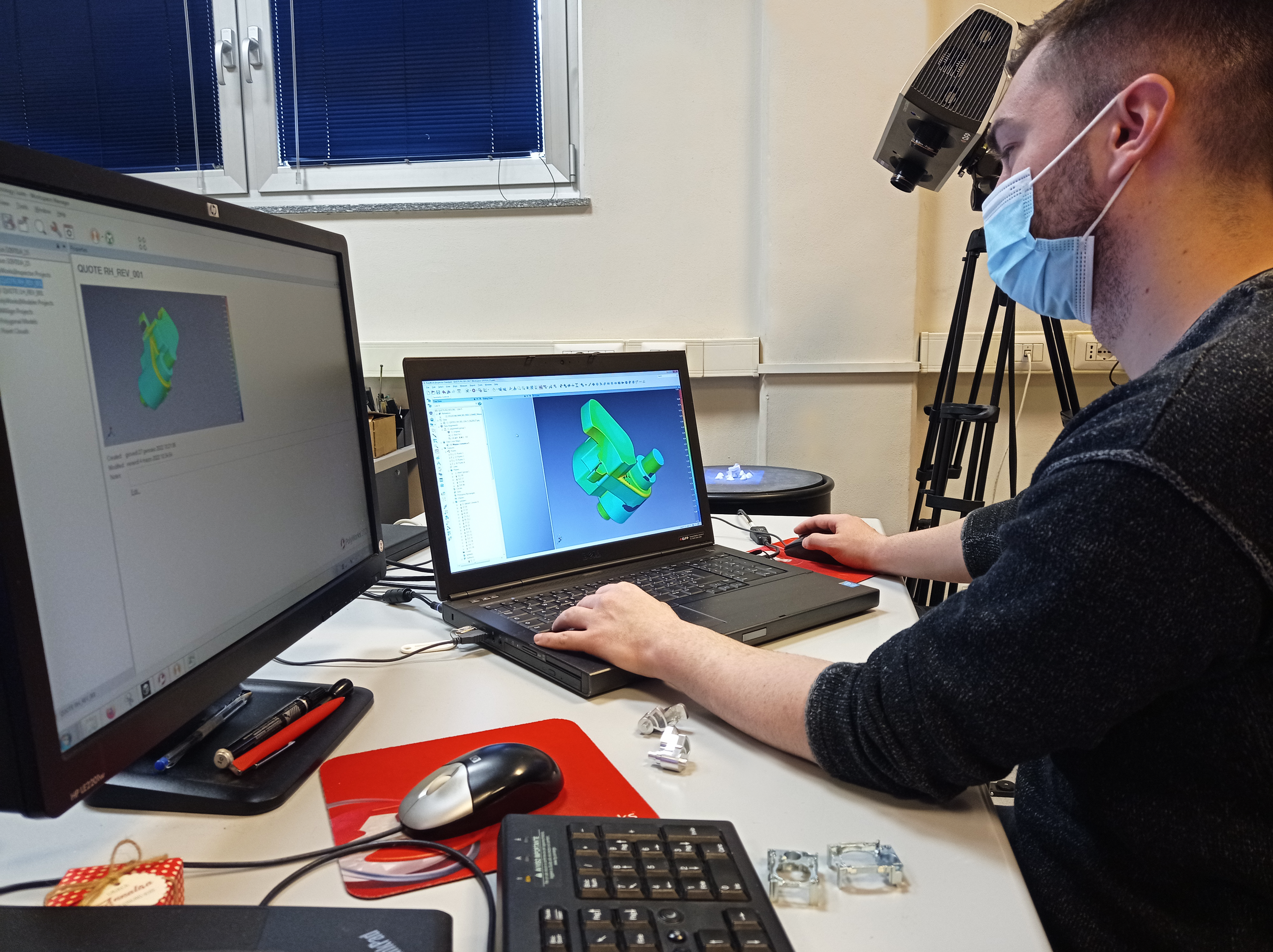
Industry 4.0 tries to gather every phase of production process into simulation. In particular in die casting engineering, simulation has to consider several points: productive plant, die casting tools, automation tools, cooling tools, secondary operation tools.