All the posts for high-pressure-die-casting
Posts by Topic
- Die Casting simulation (35)
- Co-design (26)
- Cost reduction (23)
- die casting finishing (18)
- Defects reduction (16)
- high pressure die casting (16)
- die casting process (15)
- VAVE (13)
- die casting (12)
- Zinc (11)
- Zinc benefits (10)
- casting process (10)
- die casting engineering (10)
- optimization (10)
- Innovation (9)
- automotive (8)
- casting (8)
- ZAMAK (7)
- product design (6)
- quality (6)
- Mould Design (5)
- Scrap reduction (5)
- automation (5)
- saving (5)
- Mold (4)
- benefits (4)
- die casting machines (4)
- hot chamber die casting (4)
- industry (4)
- supply chain (4)
- zinc alloys (4)
- Commodity (3)
- coffee market (3)
- mold maintenance (3)
- process improvement (3)
- small appliances (3)
- technology (3)
- thin wall thickness (3)
- Shrinkage porosity (2)
- costs saving (2)
- customer service (2)
- cycle time (2)
- electronic products (2)
- improvement (2)
- metrology (2)
- mold design (2)
- process analysis (2)
- production (2)
- production process (2)
- recycling (2)
- sustainability (2)
- white goods (2)
- zinc life cycle (2)
- DFM (1)
- Electromechanical systems (1)
- HPDC (1)
- Lighting components (1)
- Press (1)
- SME (1)
- Textile (1)
- Textile Machineries (1)
- Zinc alloy actuators (1)
- actuators (1)
- chrome plating (1)
- environment (1)
- industrial machinery (1)
- industrialization (1)
- lead time (1)
- machines (1)
- painting (1)
- quality control (1)
- surface treatment (1)
- tier 2 automotive supplier (1)
- vacuum valve (1)
- zinc alloys for doors and windows (1)
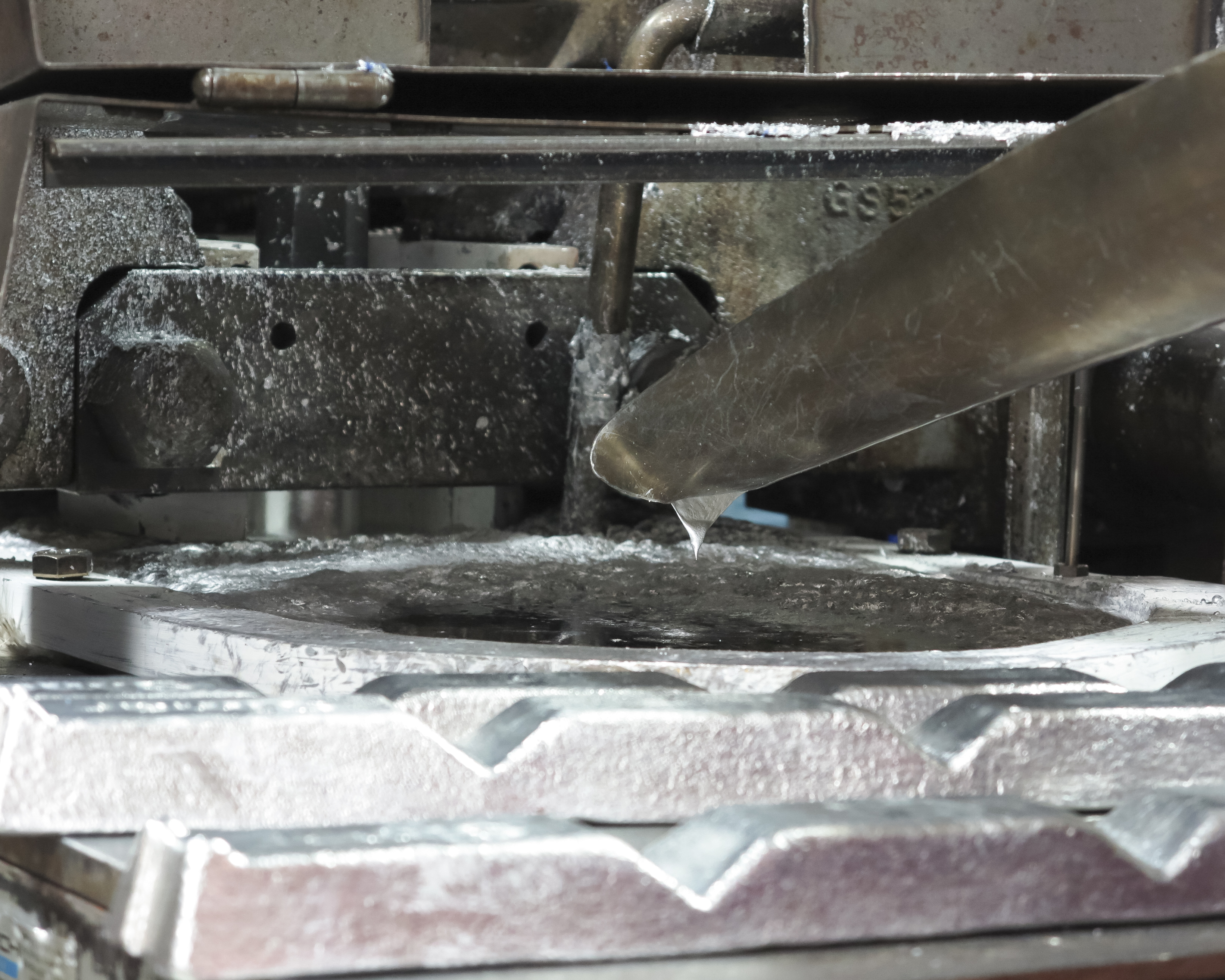
This post deals with the fundamentals of die casting machines and their role in the whole die casting process. Moreover, the post gives an outlook on the sector's future perspectives.
Thanks to their excellent mechanical and physical properties zinc alloys are a perfect material for die casting: they are indeed resistant, fluid, durable and rigid. But which are the best zinc alloys for hot chamber die casting? In this post we are going to analyze the different characteristics of zinc alloys for hot chamber die casting in order to define the best choice on the basis of the features that the final product requires.
In this post we are going to analyze a case study that explains how to reduce casting defects through mold design. Due to mold wear condition components started to show superficial defects: Bruschi engineers have thus introduced improvements in order to reduce casting defects.
In this post we are going to explore two case study: the first one is dedicated to resolving issues with die maintenance for a component of automotive sector, while the second one regards the optimization of set up parameters for a component of small domestic appliances.
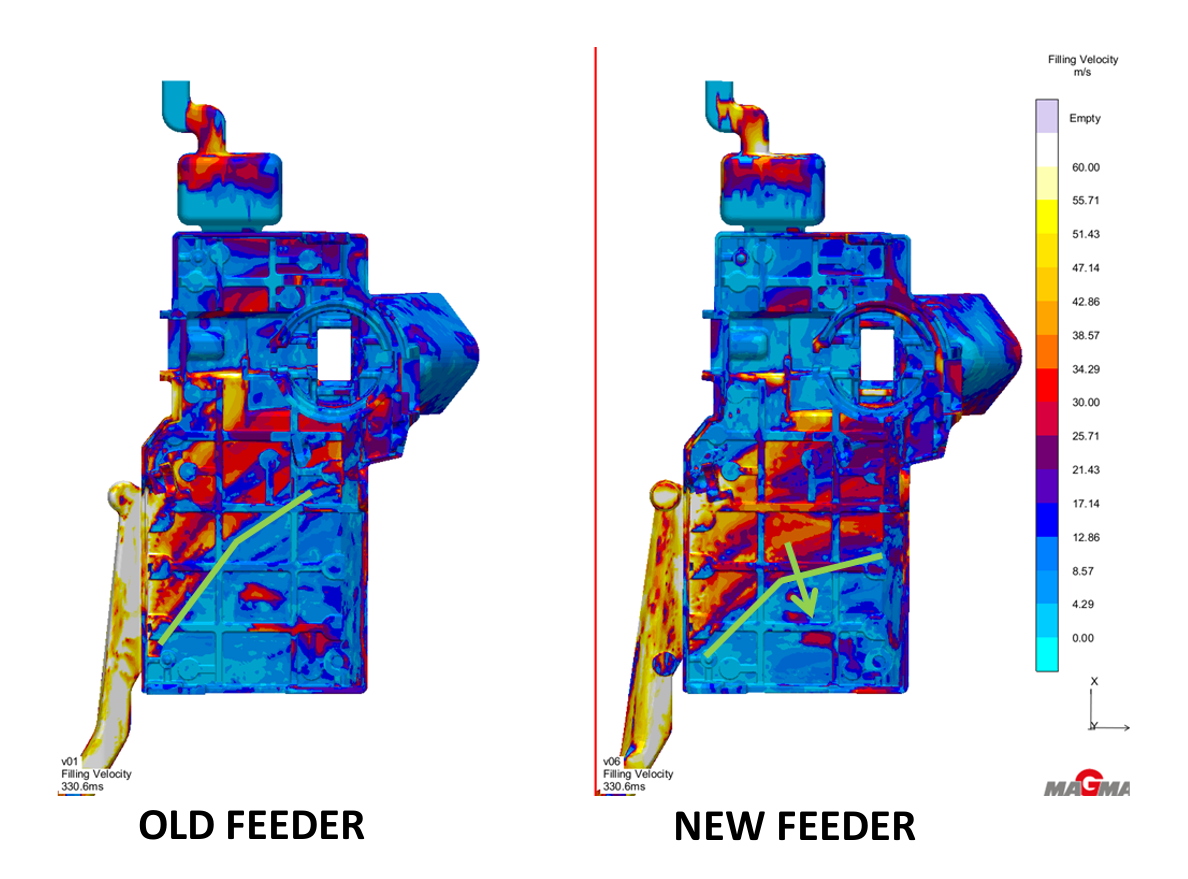
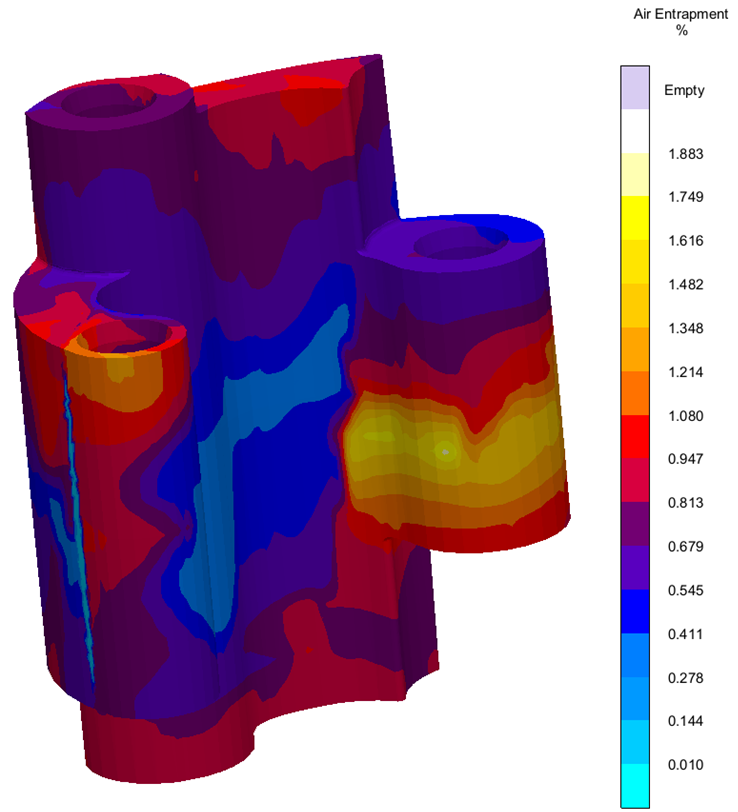
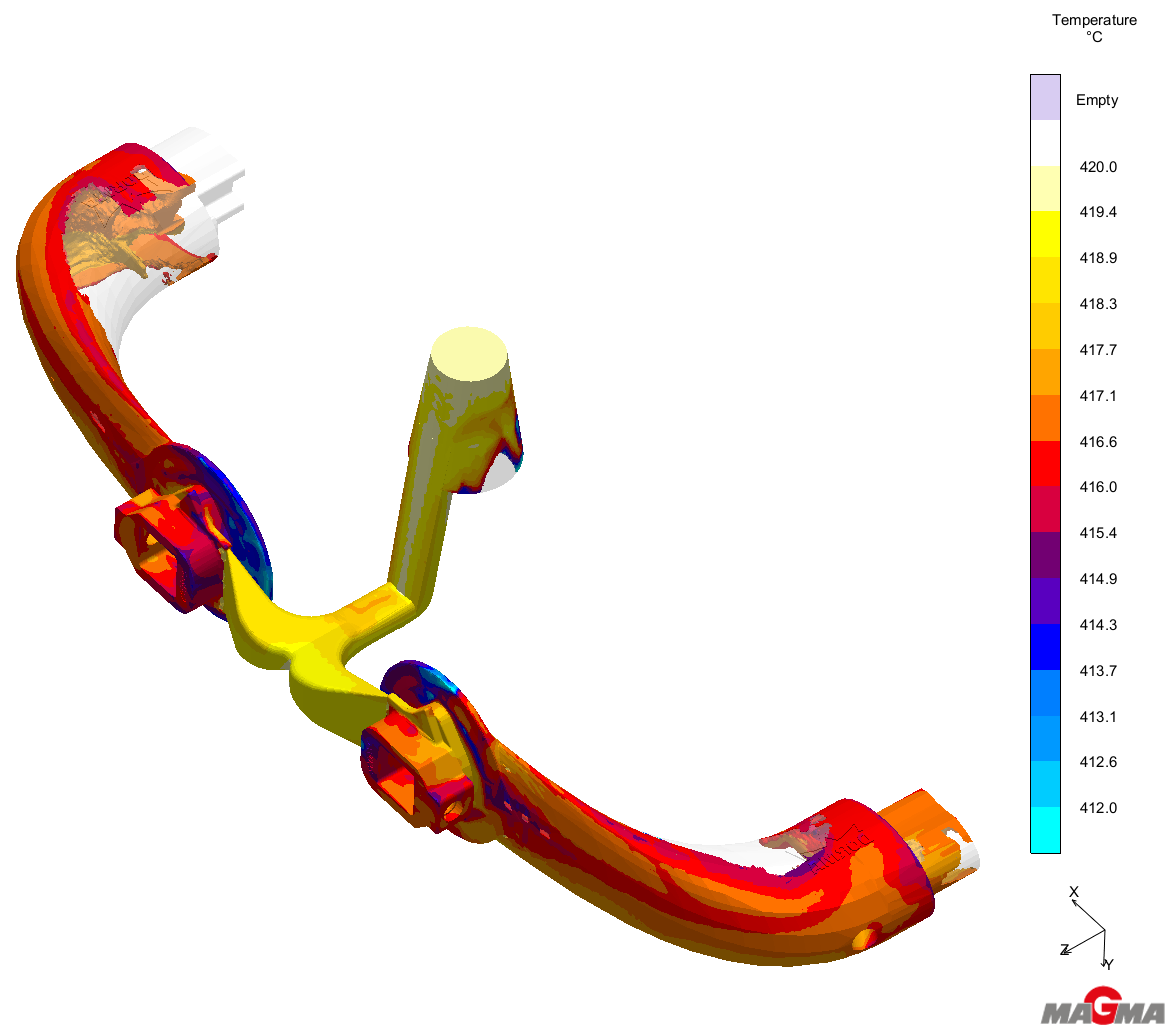
In this post we are going to explore a case study dedicated to the improvement of mechanical characteristics, by reducing shrinkage porosity in a component for building sector. This post is part of a series in which we explain the importance of simulation for HPDC (High Pressure Die Casting) through the presentation of real life cases.
The process of zinc die casting is highly popular for making parts in building and industrial fields, but its most common application is in automotive industry. In fact, cars have different parts that can be crafted through die casting, so much that the modern process of die casting originally started for automotive industry.
In this series of posts, we are going to explain the importance of simulation for HPDC (High Pressure Die Casting) through the presentation of different case studies, in which simulation played a crucial role.
In this post we are going to list and define the most common surface treatments for zinc die casting and their effects, and we are going to present three case studies in which the application of a specific treatment helped in improving the overall performance of the component.
In this post we are going to list the most common defects in zinc die casting surface treatments and explain how to prevent them. We are going to analyze the following defects: blisters, pitting, burnings, nodules and flaking.
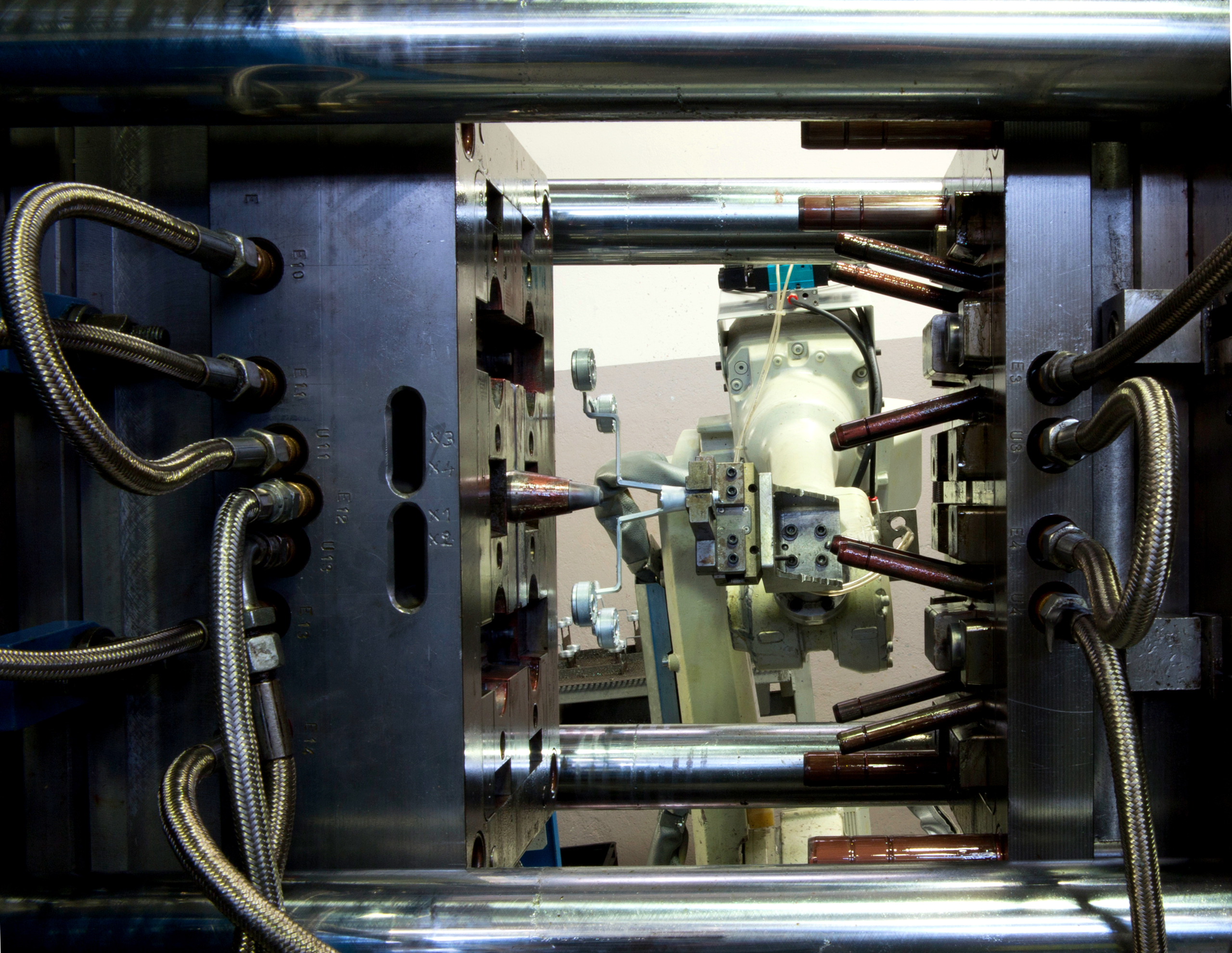
In the current industrial context, reducing production times will become ever more crucial to offer customers an optimal product in the shortest time possible, with consistent cost savings.